This post introduces us to one of the most major and important device of the defense systems “RADAR”.
INTRODUCTION
Radar stands for radio detection and ranging systems. These are devices or instruments which are used to detect the speed, range and even the speed of the bodies. Radar transmits electromagnetic signals in air at different wavelengths and its receiver listens for the reflected echoes that are when the transmitted signal contacts with an object, the object reflects the signal and the receiver of the radar listens for this reflected signal from which it determines the speed and distance of the object.
The signal from the radar travels with the speed of light= 3 x 108 m/sec. The radar calculates the time taken from the instant the signal is transmitted and the time signal received and then there is just a simple primary concept of distance= speed x time, and the distance of the target object is calculated.
HISTORY OF RADAR
The radar has its historical importance, invented and developed by Germany and England. It has great role to let the English win over the Germans. The English with the help of radars detected the coming of German aircrafts much earlier and get prepare themselves for a response attack and even to bring down German stukas.
APPLICATIONS OF RADAR
Radar has various applications including
· Aircraft altimeters which are used to detect the distance of the flight from the ground
· Whether forecasting as radars can be used to detect the position of the clouds
· Traffic control on roads by detecting speed of high speed moving vehicles
· Military purposes as they are used to detect enemy ships and aircrafts. Also radars are used as missile guidance radars
Components of radar
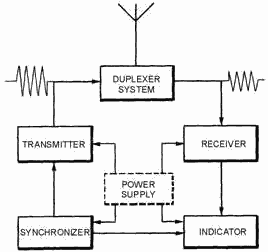
Radar consists of following components:-
Transmitter: – It creates the radio wave to be sent and modulates it, amplifies it and transmits it at a certain high power. Various microwave devices such as klystron, magnetron, TWT are used to generate these waves.
Receiver: – It is a very sensitive device especially to high frequencies, it receives the signal and amplifies the weak reflected signal.
Antenna: – the antenna takes the radar from transmitter and puts it into air and similarly gets the reflected signal from air to receiver.
Duplexer: – this is a switching device which alternately connects to transmitter and receiver. Its purpose is to protect receiver from high power of the transmitter.
Synchronizer:- it coordinates the timing for range determination. it regulates the rate at which pulses are sent
Power supply:- it provides electrical power for all the components. The largest consumer of power is transmitter.
Display: – The display unit shows the various form of signals received for the operator to understand them examples are PPI, RHI, FPD etc.
TYPES OF RADAR
Radar is generally categorized into two types according to the type of signal they transmit.
1) Pulse wave radar: – it transmits pulses of signals with a certain time interval between two pulses.
2) Continuous wave radar: – it transmits a continuous wave and looks for change in frequency. These radars function on the principle of Doppler Effect.
Doppler Effect in detail
In our everyday life we have multiple examples of Doppler Effect; the whistle from a moving train is an example. As a train approaches a stationary listener , the pitch of the whistle sound gets higher and as the train passes the stationary listener the sound of the train whistle gets decreasing.
Scientifically, if either source of oscillation or observer of oscillation is in motion an apparent shift in frequency takes place.
Practical radars
The above explained till now is simply the basic radar. But practically radars have to deal with a lot of noise. It could be noise in the receiver possibly due to various microwave components or clutters which is the noise generated by natural environment.
Radar below sea level
Radars cannot work underwater as radar transmits electromagnetic pulses which get attenuated or short in water as sea water is saline and a good conductor of electricity.
Hence sonars are used which instead of electromagnetic waves uses sound waves.
A discussion on Radars in daily use is here on how RADARS are present in our cars see:-driving with RADARS
Subscribe Author for Updates
http://Inteligentcomp.com